Most of Us Still Don't Know What We're Doing: The Hard Truth About AI
\Two years after ChatGPT's release, a sobering reality emerges: despite AI's growing influence, only 9% of workers truly understand and effectively use AI tools. While Microsoft and Google promise AI agents that can save millions and replace hundreds of workers, the reality shows a stark disconnect between hype and implementation.
The AI Proficiency Report created by the Section, analyzed over 5,000 knowledge workers across the US, UK, and Canada, and reveals critical gaps in deployment, training, and practical application.
Companies face a pivotal challenge - 47% of their workforce barely grasp AI basics, while 11% actively avoid it. Even in organizations openly embracing AI, manager scepticism cuts expert-level usage in half. The report has covered many more things; let's look into those and try to get a better idea about the present AI era.
Let's get started.
The Reality Check
Only 9% of workers truly understand and use AI effectively in their daily tasks. Big companies like Microsoft and Google are making big promises about AI agents that could save millions and replace hundreds of workers, but the reality is quite different. Their claims about fully automated AI workflows are likely 3+ years away from becoming real for most businesses.
Most organisations are stuck in what experts call "AI theater" - making noise about AI without creating real change.
Companies invest heavily in AI tools but fail to train employees properly
Leadership often focuses on quick wins instead of long-term AI integration
Basic AI tasks get labelled as "transformation" while core processes remain unchanged
The most interesting finding is that company size doesn't determine AI success. Whether it's a small startup or a large corporation, what really matters is how much support managers give to AI initiatives. When leaders actively back AI projects and provide resources, teams adapt better.
In the study conducted by the Section over 5,000 workers across the US, UK, and Canada, interesting patterns are revealed.
Nearly half of workers (47%) are just beginners with AI
Even in companies that ban AI, 43% of workers use it weekly
Manager support doubles the number of skilled AI users in organisations
These findings suggest we need less hype and more practical steps to make AI work in real business settings.
Most companies lack proper AI training programs for their employees
Current AI tools need human guidance through careful prompting
Leaders often rush into AI without proper planning or support systems
The Current State of AI Proficiency
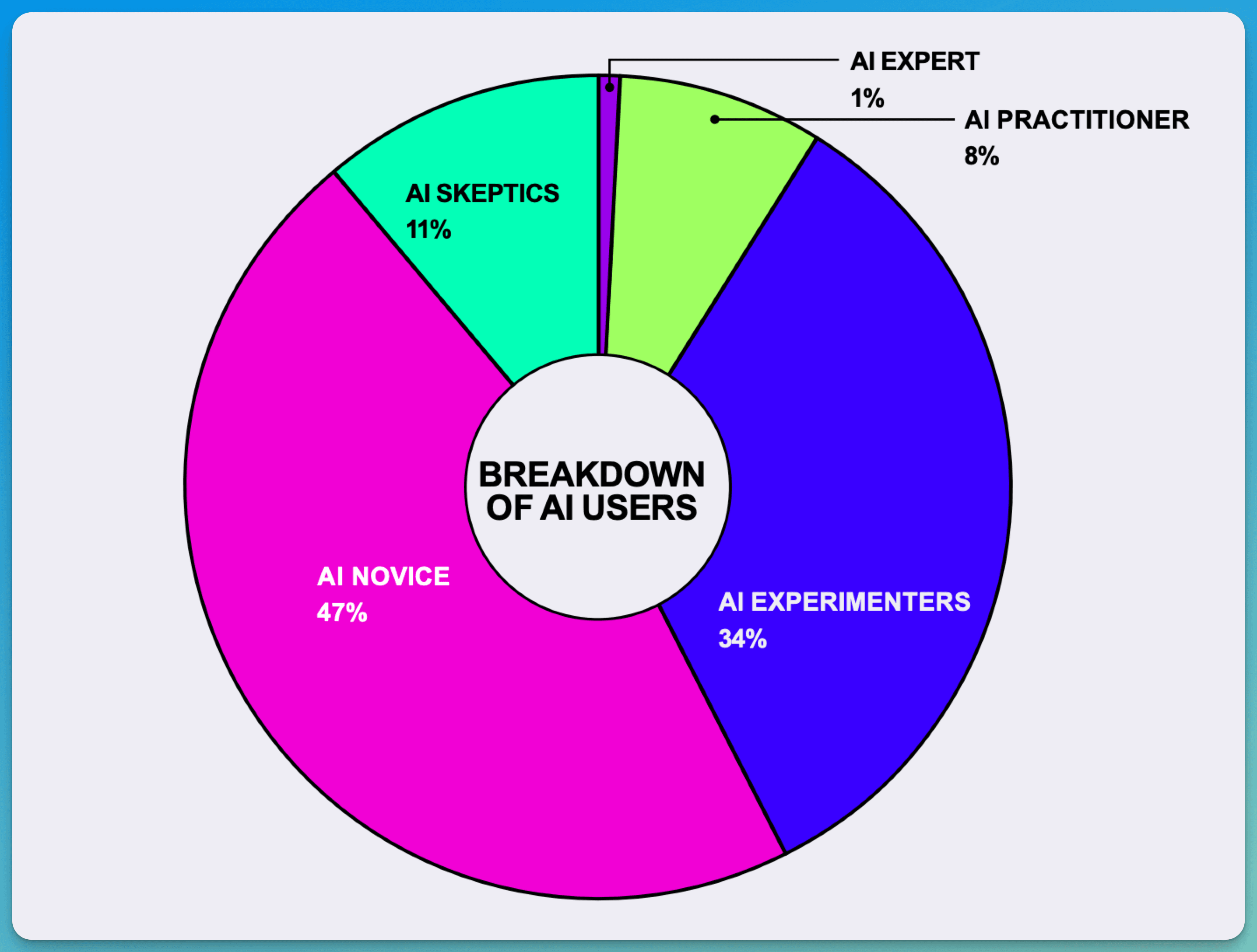
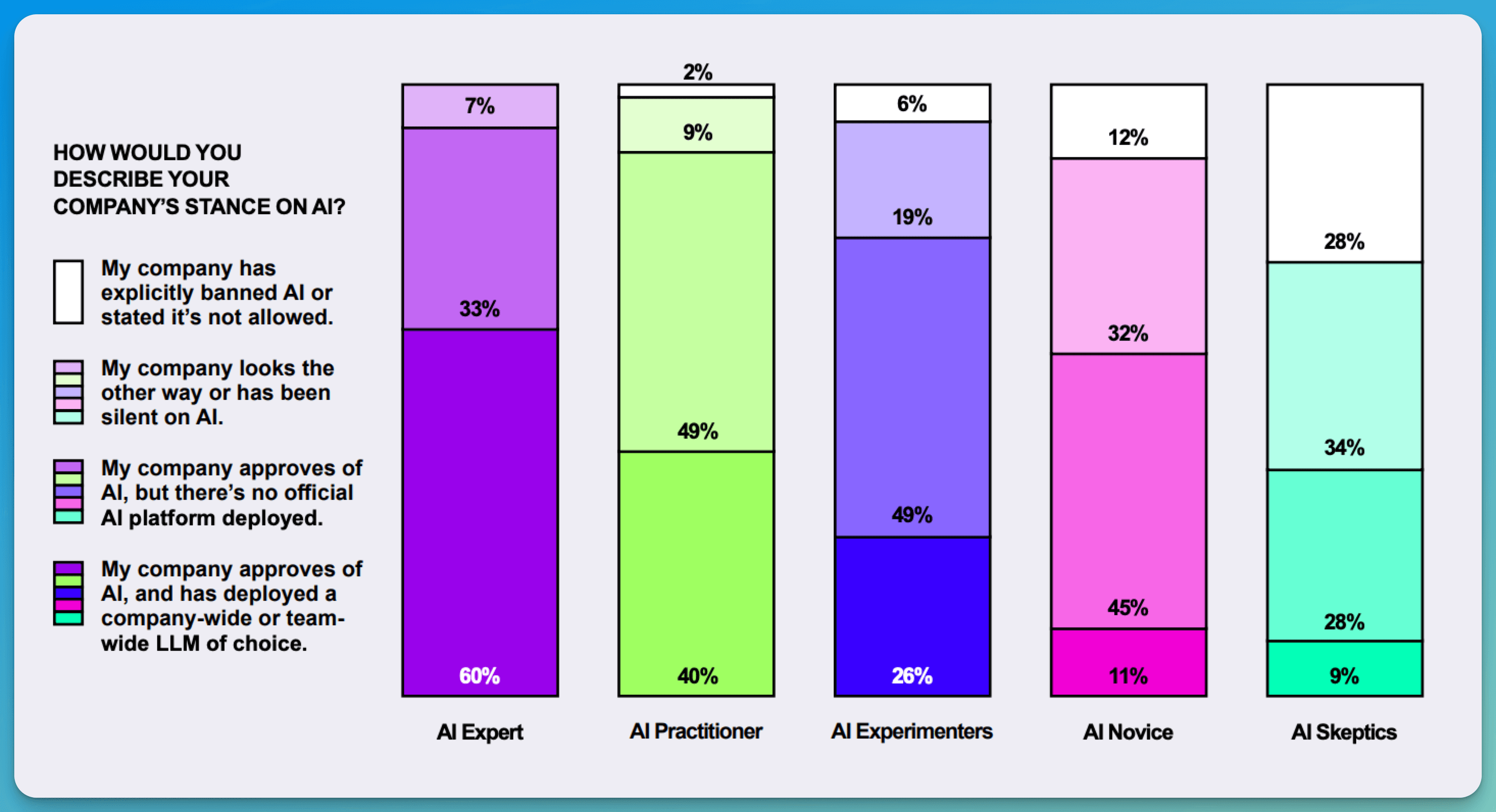
The study made by the Section reveals five distinct groups of AI users in today's workplace. At the top, only 1% are true AI Experts who deeply understand AI's capabilities and can create complex workflows. These rare specialists often lead AI initiatives and train others in their organizations.
AI Experts handle advanced tasks like process automation and data analysis
They understand AI's limitations and potential risks thoroughly
These specialists often become internal AI advisors for their teams
The Practitioners, making up 8% of workers, use AI effectively for daily tasks. Meanwhile, Experimenters (34%) show enthusiasm but struggle with consistent results. They try different AI tools but often miss opportunities for deeper integration.
Practitioners focus on practical AI applications like content creation
Experimenters face challenges with prompt engineering
Both groups need more structured guidance for better results
The largest group, Novices (47%), barely use AI tools, while Skeptics (11%) actively avoid them. Novices often lack confidence and proper training, using AI for basic tasks only.
Most novices stick to simple tasks like summarization
Skeptics often cite concerns about accuracy and job security
Both groups need clear examples of AI's practical benefits
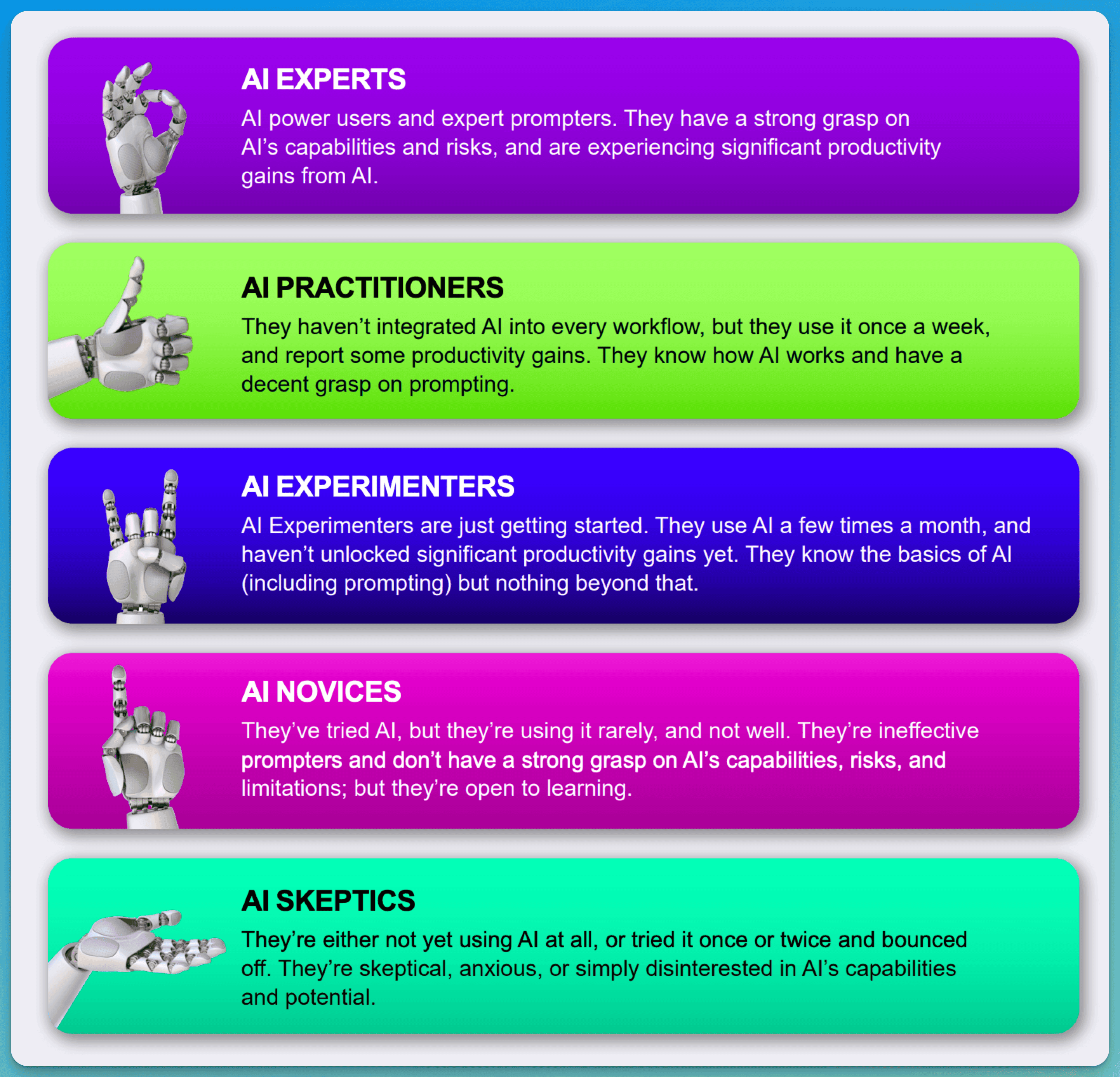
This distribution shows a clear need for better AI training and support across all levels.
Tech companies aren't that far ahead
Even in the tech sector, only 20% of employees show real AI proficiency. This surprisingly low number challenges the assumption that tech companies lead in AI adoption.
Tech companies struggle with consistent AI training programs
Most tech employees use basic AI features rather than advanced applications
The gap between leaders and workers creates implementation barriers
Senior leaders show higher AI proficiency than junior staff, creating an unusual dynamic. While 35% of senior leaders qualify as AI Practitioners or Experts, only 15% of junior employees reach this level.
Senior leaders often have better access to AI training resources
Junior staff frequently lack guided practice opportunities
This knowledge gap slows down company-wide AI adoption
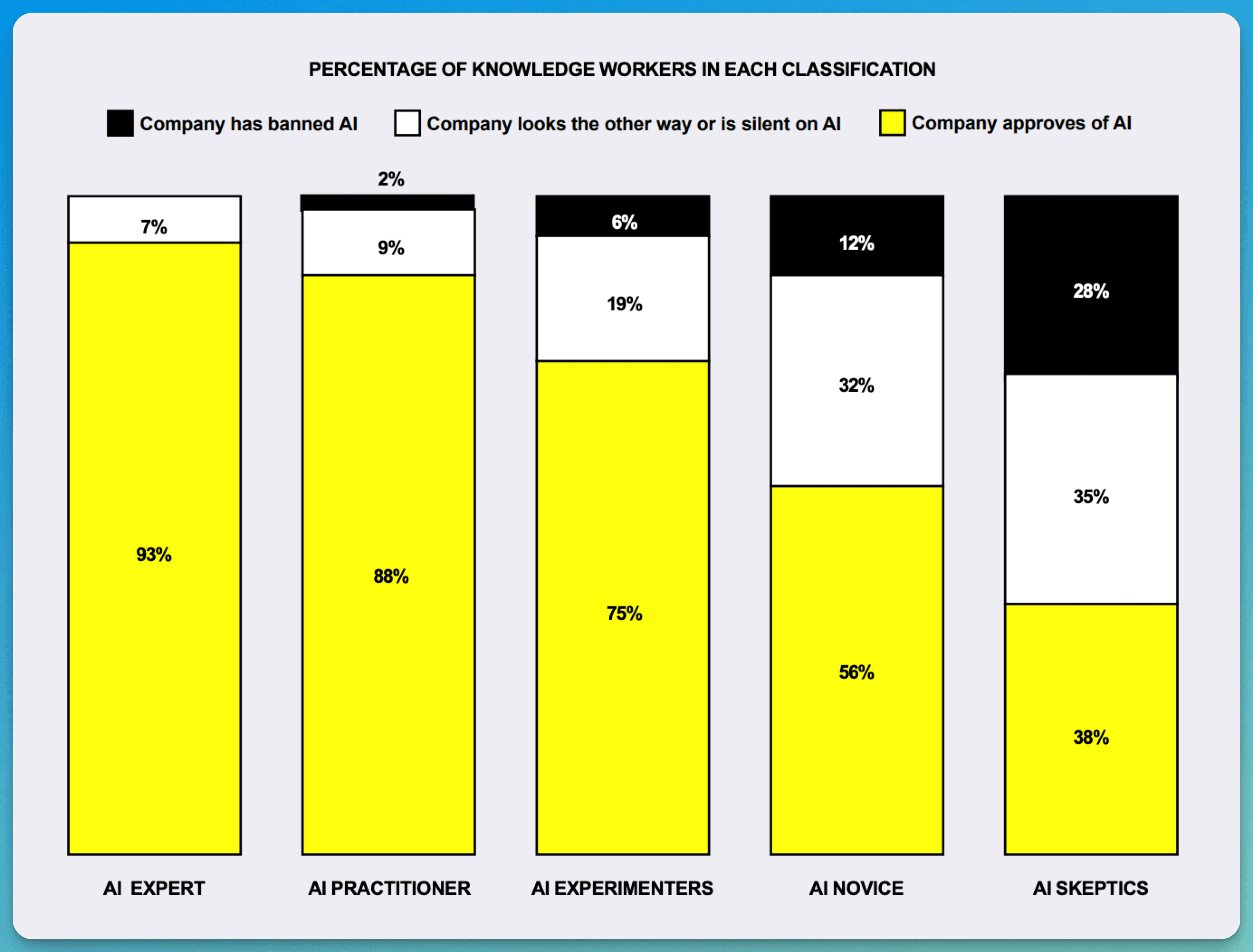
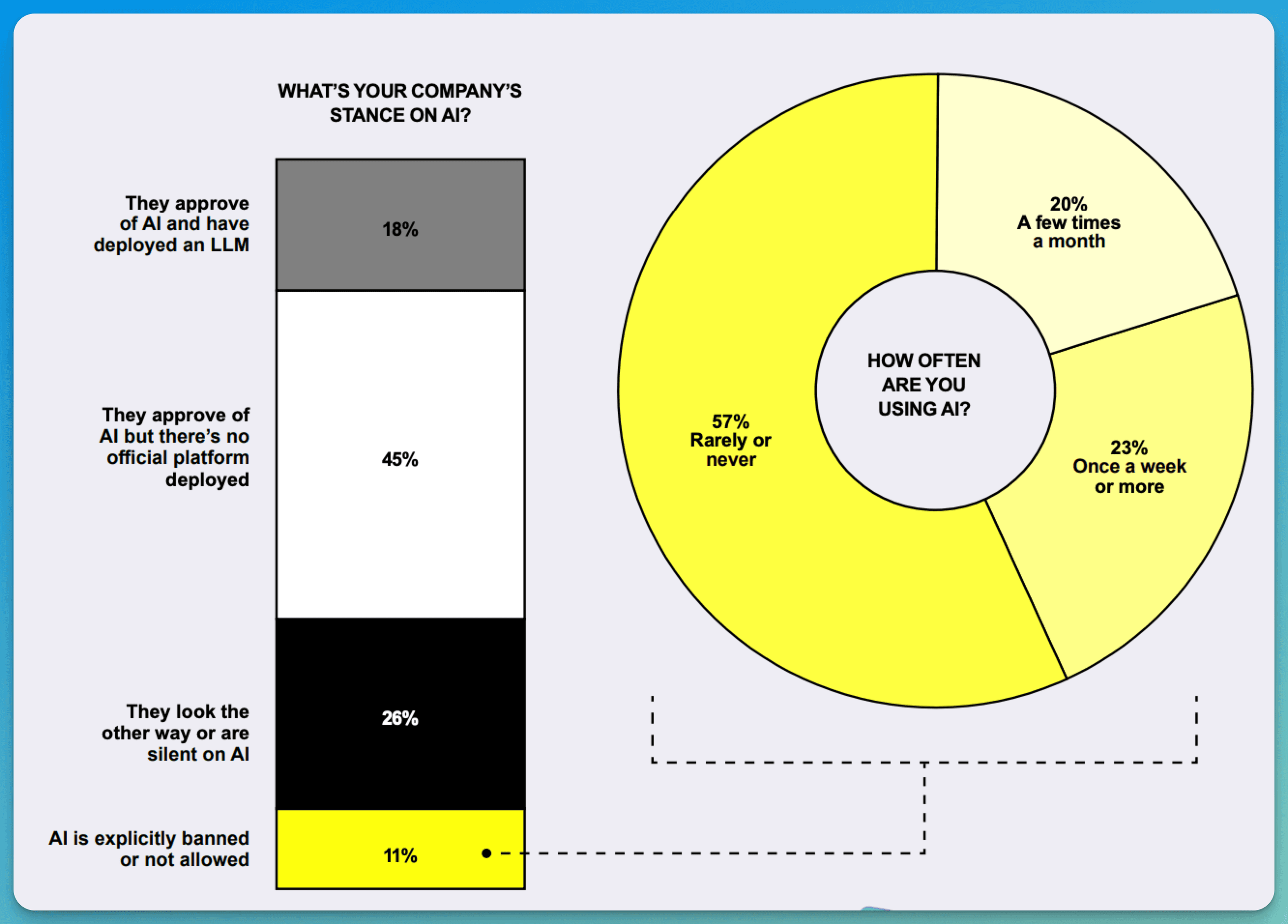
Company AI bans prove largely ineffective. Data shows 43% of employees in companies with AI restrictions still use these tools weekly.
Employees find ways around AI restrictions to meet productivity demands
Unofficial AI use creates security and compliance risks
Companies need realistic AI policies that balance safety with productivity needs
What's Actually Working
Based on the AI Proficiency Report by the Section, here's what's working in AI implementation:
Key Success Factors:
Company-deployed LLMs lead to higher proficiency - 60% of AI Experts have access to company platforms versus just 11% of Novices
Manager support directly impacts success - Companies with supportive managers have 2x more AI Experts/Practitioners than those without
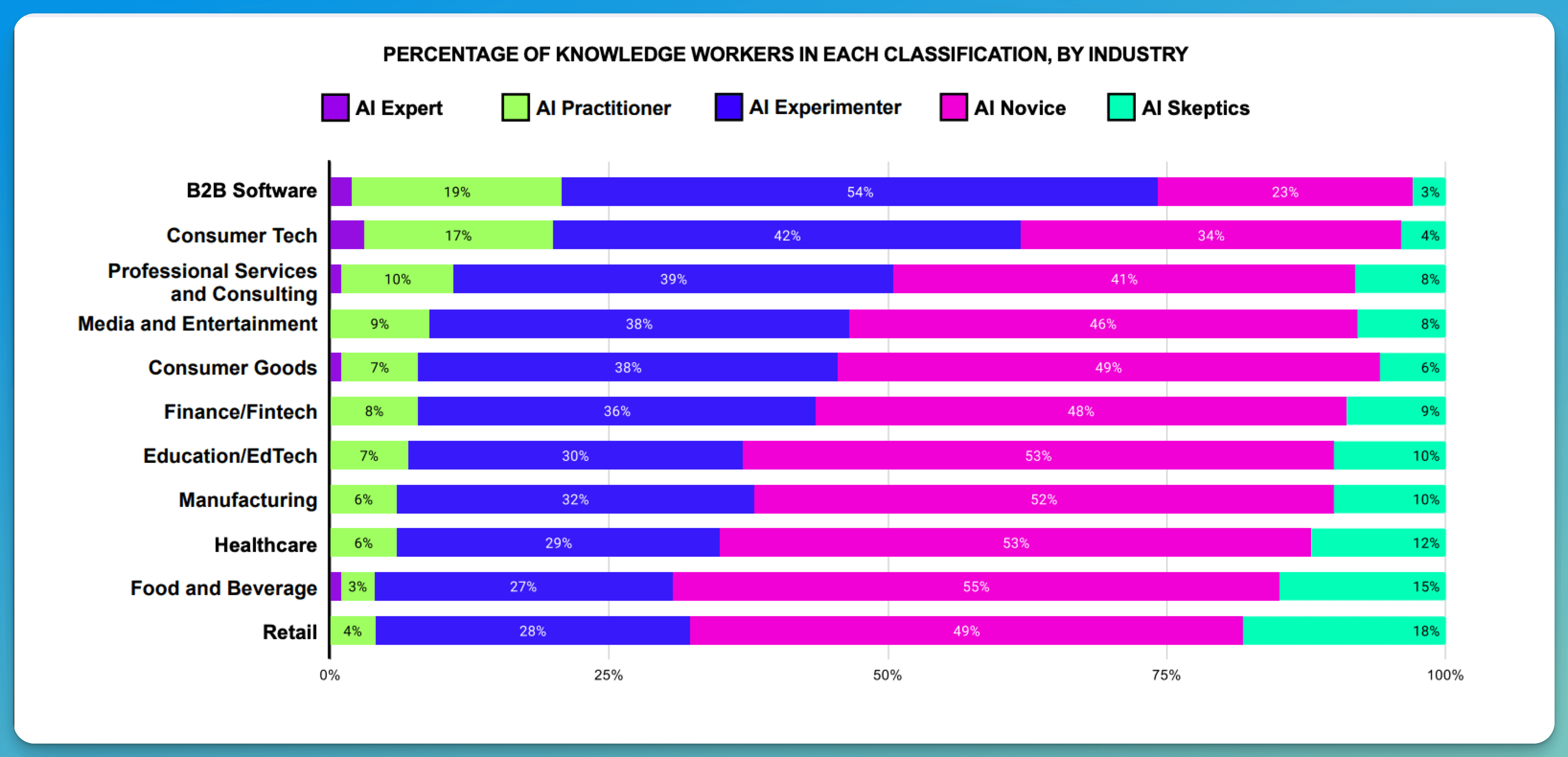
Language-intensive industries show the highest adoption - Tech, consulting, and media companies have 20% of employees at the Expert/Practitioner level
Real Benefits:
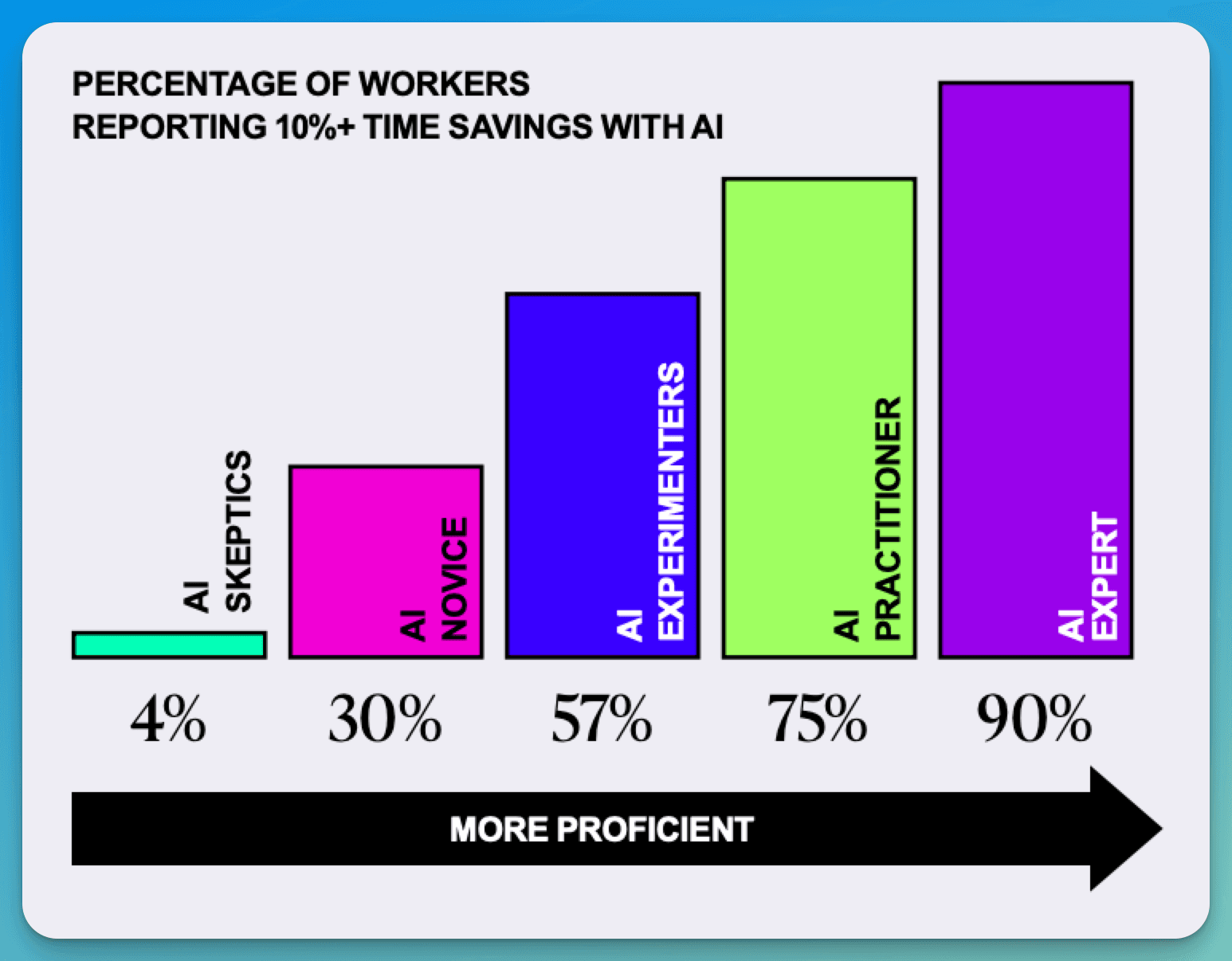
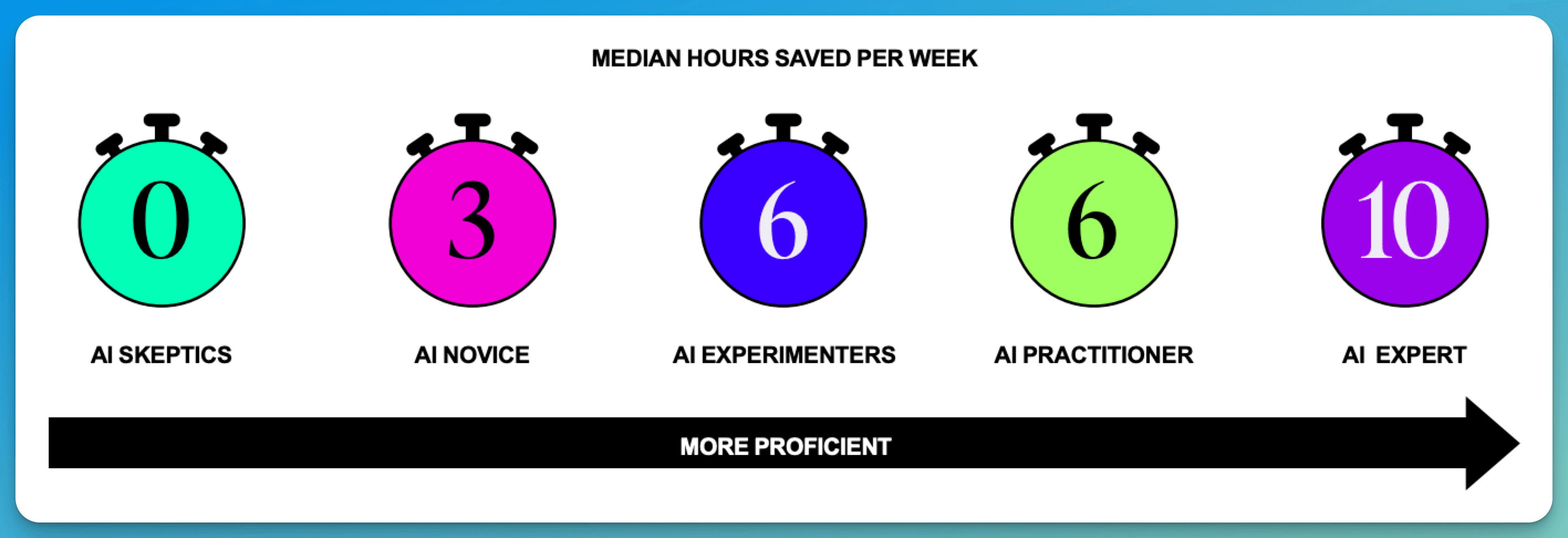
AI Experts save 10+ hours per week (90% report significant time savings)
Practitioners achieve 6+ hours in weekly time savings
Moving from Novice to Experimenter doubles productivity gains
Success Pattern Examples:
B2B Software companies lead with 19% Expert/Practitioner rates through structured deployment and training
Professional services firms achieve 10% Expert/Practitioner rates by focusing on language-intensive workflows
Companies that combine clear AI policies, manager support, and hands-on training see 2-3x higher proficiency rates
The key differentiator is having a comprehensive approach that includes proper tools, clear policies, supportive management, and practical training - rather than just deploying technology alone.
The Training Problem
Current AI training programs are falling short, with only 24% of employees receiving any AI training from their companies. The data reveals critical gaps between deployment and effectiveness.
Core Issues:
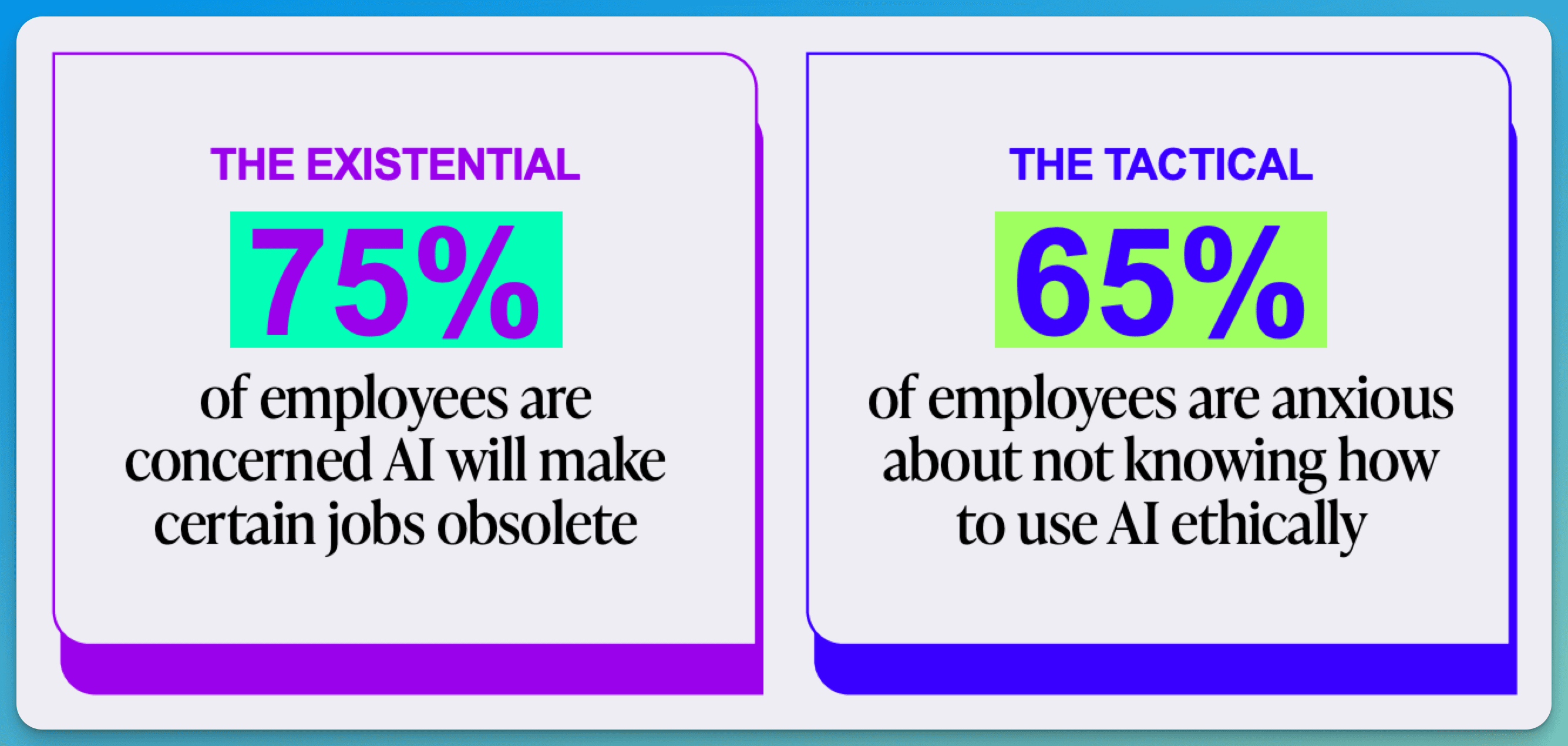
Existential Anxiety: 75% of employees fear AI will make jobs obsolete
Tactical Concerns: 65% worry about using AI ethically
Training Gap: Only 24% have received formal AI training
CurrentShortcomings:
Training focuses on policies rather than practical skills
No meaningful difference in AI knowledge scores between trained (4.5/10) and untrained (4.8/10) employees
Companies prioritize leadership training while neglecting frontline workers
77% of AI Novices receive no training despite handling crucial operational tasks
Current Training Effectiveness (Scale 1-10):
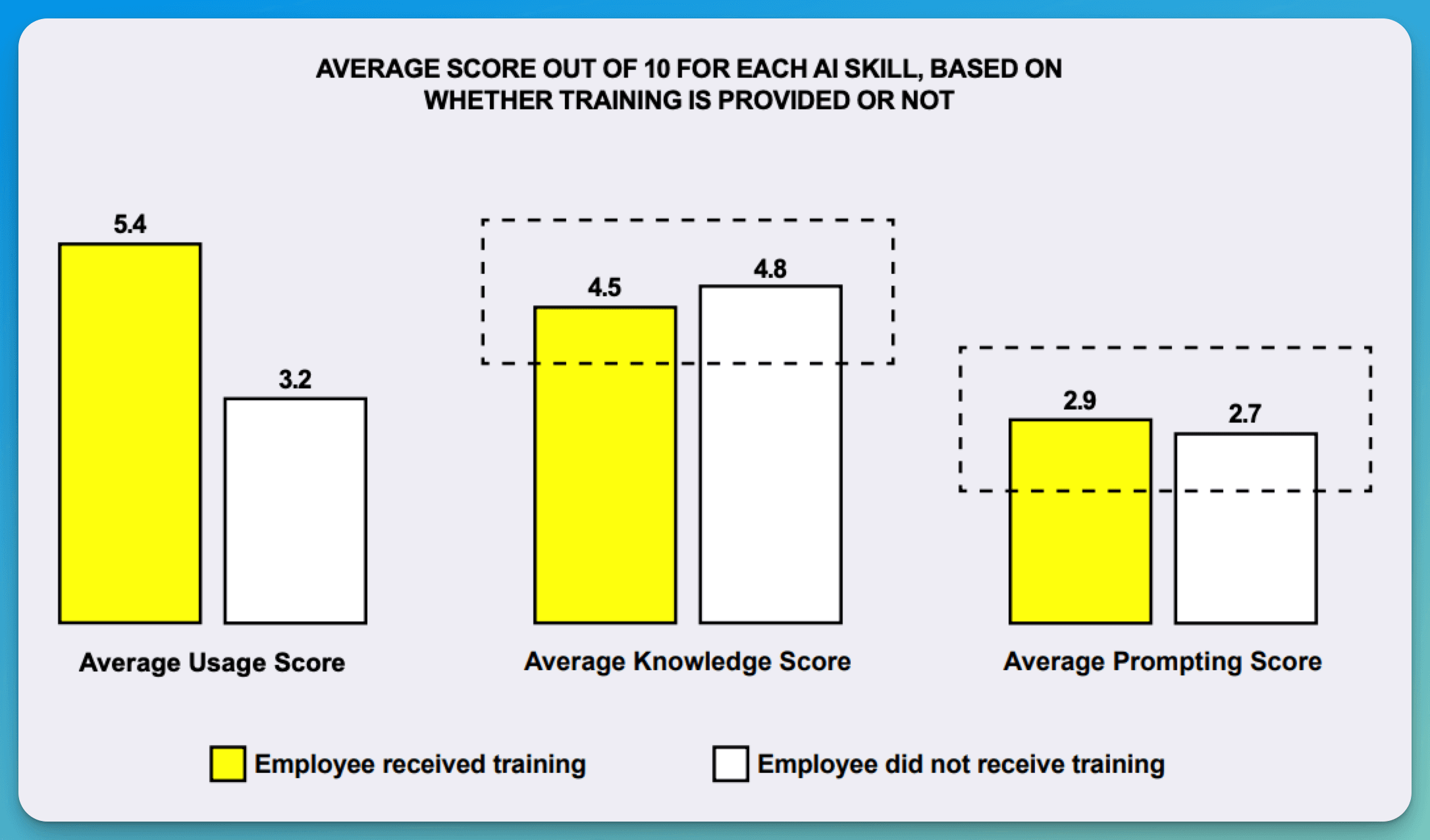
Usage Score: Trained (5.4) vs Untrained (3.2)
Knowledge Score: Trained (4.5) vs Untrained (4.8)
Prompting Score: Trained (2.9) vs Untrained (2.7)
Most importantly, employees continue to use AI tools despite company restrictions, creating significant security vulnerabilities. While 11% of organizations ban AI outright, 43% of their employees still use unauthorized tools, primarily free LLMs lacking proper security controls.
45% use unauthorized free AI tools regularly
Most lack training in data privacy settings
Sensitive company data faces exposure risk
Security measures often go unimplemented
This shadow usage particularly threatens companies handling sensitive data and regulated information. Without proper controls or training, employees unknowingly create security gaps while trying to improve productivity.
Conclusion
The coming year will mark a decisive turning point in AI adoption, with industry leaders rapidly pulling ahead while unprepared companies fall behind. Data shows that only 18% of companies currently have deployed enterprise AI platforms, but by 2025, we expect to see 2-3 companies per sector emerge as truly AI-native organizations, achieving over 80% workforce proficiency.
These leaders will leverage comprehensive training programs, clear policies, and enterprise-wide AI platforms to create substantial productivity advantages. The gap between AI-native companies and those still struggling with basic implementation will widen dramatically, as effective AI use can save up to 10 hours per week per employee.
To prepare, leadership teams must immediately focus on three critical areas: implementing secure enterprise-wide AI platforms, developing comprehensive training programs that go beyond compliance, and establishing clear usage policies that address both technical and ethical concerns.
Most importantly, they need to move quickly from theoretical interest to practical implementation, prioritizing the progression of employees from Novice to Experimenter level. Companies that fail to make these transitions risk falling irreparably behind as AI-native competitors reshape industry standards and expectations.
Read AI Proficiency Report by Section
FAQs
1. Why are companies with banned AI policies still seeing high usage rates?
43% of employees in companies that ban AI still use it unofficially, mainly through free tools, creating security risks. This "shadow AI" usage stems from productivity needs, despite lacking proper training and controls.
2. How much difference does AI training actually make?
Current training shows minimal impact - trained employees score only slightly better (4.5 vs 4.8) in knowledge and prompting than untrained ones. Training focuses too heavily on policy compliance rather than practical skills.
3. Why do senior employees show higher AI proficiency than junior staff?
Senior staff receive better access to AI tools and training, with 12-13% reaching the Expert/Practitioner level versus 5% of junior staff. They also face less job security anxiety about AI adoption.
4. What's the real productivity difference between AI experts and novices?
AI Experts save approximately 10 hours weekly, while novices report minimal time savings. Experts (90%) consistently achieve 10%+ time savings compared to novices (30%).
Comments
Your comment has been submitted